Recombinant anti-mouse IL-2 antibody - Clone S4B6 (D265A)
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 Recombinant mAb against mouse IL-2 (clone S4B6), D265A effectorless. For in vitro use |
Show product |
200 µg |
mil2-mab15-02
|
|
||
|
Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 InvivoFit™ Recombinant mAb against mouse IL-2 (clone S4B6), D265A effectorless. For in vivo use |
Show product |
1 mg |
mil2-mab15-1
|
|

InvivoGen’s engineered Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 antibody
 InvivoGen also offers:
InvivoGen also offers:
Recombinant mouse IL-2 antibody
InvivoGen provides a recombinant murinized anti-mouse IL-2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that was previously extracted from hybridoma. It is now expressed and produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, ensuring reliability and lot-to-lot reproducibility. Thereby, common hybridoma-related drawbacks such as the generation of non-relevant mAbs containing aberrant light chains are avoided [1].
Additionally, the rat-derived constant region was replaced by a murine constant region, making the mAb ~65% of murine origin. This mAb now consists of the variable region of a rat anti-mIL-2 mAb (clone S4B6) and the engineered murine IgG1e3 constant region. Within the IgG1e3 isotype, a point mutation D265A was introduced leading to a complete loss of unwanted Fc-associated effector functions [2]. Altogether, these alterations increase antibody performance and overcome immunogenic events, especially in vivo [3].
While the S4B6-derived mAb shows neutralizing activities in vitro, it has been reported to boost NK cell and memory CD8+ T cell numbers through the formation of an immune complex with IL-2 (IL2C) in vivo [4].
InvivoGen provides this antibody in two grades:
- In vitro use: Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3
- In vivo use: Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 InvivoFit™
All InvivoFit™ products are handled in a clean room, filter-sterilized, and tested for bacterial contaminants. Additionally, this grade guarantees low levels of endotoxins (<1 EU/ml). The buffer formulation is specifically adapted for in vivo studies.
Key features:
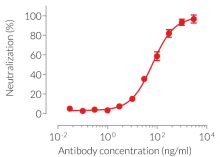
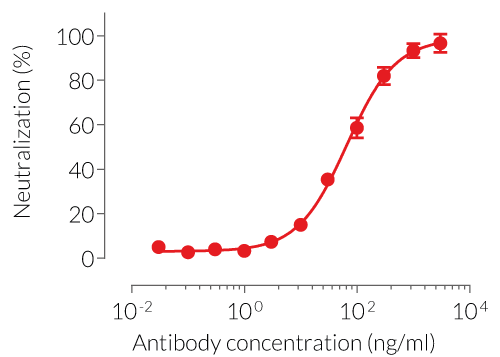
- Potent and specific neutralization activity against mIL-2 in vitro
- Sequence is 65% murine
- Murine IgG1e3 isotype (constant region)
- mIgG1e3 (IgG1 with a replacement of aspartic (D) acid by alanine (A) at position 265 point mutation) is effectorless
- Free from non-relevant mAbs found in hybridoma-based productions
- Produced in animal-free facilities and defined media
- Low aggregation < 5%
- InvivoFit™ grade is available
Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 is designed to efficiently neutralize the biological activity of mIL-2 without triggering any effector functions. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and maintaining peripheral self-tolerance by having both immuno-stimulatory and -regulatory functions [5].
![]() Read our review on IL-2: The Activator and Controller
Read our review on IL-2: The Activator and Controller
References:
1. Bradbury, A. et al. 2018. When monoclonal antibodies are not monospecific: Hybridomas frequently express additional functional variable regions. mAbs, 10(4), 539–546
2. Baudino L. et al., 2008. Crucial role of aspartic acid at position 265 in the CH2 domain for murine IgG2a and IgG2b Fc-associated effector functions. J. Immunol. 181(9):6664-9.
3. Brüggemann M. et al., 1989. The immunogenicity of chimeric antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 170:2153-2157.
4. Boyman O, et al., 2006. Selective stimulation of T cell subsets with antibody-cytokine immune complexes. Science. 2006 Mar 31;311(5769):1924-7.
5. Pol JG, et al., 2020. Effects of interleukin-2 in immunostimulation and immunosuppression. J Exp Med. 217(1):e20191247.
Specifications
Target: Murine IL-2 (mIL-2)
Specificity: No cross-reactivity with human IL-2
Clone: S4B6
Source: CHO cells
Isotype: Murine IgG1e3 (D265A mutation; no effector function), kappa
Control: Murine IgG1e3 Isotype Control
Formulation of Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3: Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered solution in a sodium phosphate buffer with glycine, saccharose, and stabilizing agents.
Formulation of Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 InvivoFit™: Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered solution in a sodium phosphate buffer with 5 % saccharose
Tested applications: Blocking & Neutralisation
Quality control:
- These products have been validated using neutralization cellular assays.
- The complete sequence of these antibodies has been verified.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
- The endotoxin level in Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 InvivoFit™ is <1 EU/mg (determined by a LAL assay).
Contents
Please note: Each mAb is sold separately. See TDS for the exact contents.
Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3
- mil2-mab15-02: 200 µg, lyophilized
Anti-mIL-2-mIgG1e3 InvivoFit™
- mil2-mab15-1: 1 mg, lyophilized
- mil2-mab15-10: 10 mg, lyophilized
![]() The product is shipped at room temperature.
The product is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Store lyophilized antibody at -20 °C.
Store lyophilized antibody at -20 °C.
![]() Lyophilized product is stable for at least 1 year.
Lyophilized product is stable for at least 1 year.
![]() Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
InvivoFit™
InvivoFit™ is a high-quality standard specifically adapted for in vivo studies. InvivoFit™ products are filter-sterilized (0.2 µm) and filled under strict aseptic conditions in a clean room. The level of bacterial contaminants (endotoxins and lipoproteins) in each lot is verified using a LAL assay and a TLR2 and TLR4 reporter assay.
Back to the topDetails
Interleukin 2
Interleukin 2 (IL-2) is a pleiotropic cytokine showing immunostimulatory or immunoinhibitory activity, depending on the target cell [1]. It is mainly produced by activated CD4+ T cells in response to antigen stimulation. To a lower extent, it can also be produced by CD8+ T cells and innate immune cells, such as activated dendritic cells (DCs), mast cells, monocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells [1]. IL-2 acts on lymphocytes by binding to the multimeric IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) and thereby engaging several intracellular signaling pathways that modulate lymphocyte survival, proliferation, and function [2].
IL-2 receptor signaling
The IL2R consists of a hetero-complex of up to three subunits: α (IL-2RA), β (IL-2RB), and γ (IL-2RG), also known as CD25, CD122, and CD132, respectively. The γ subunit CD123 is also referred to as the “common” chain (labeled “γc”), as it is shared with the receptors for IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21 [1]. Due to its high affinity, IL-2 preferentially binds to the trimeric IL-2R, which is mainly expressed on immunosuppressive regulatory T (Treg) cells [1,3]. Interestingly, IL-2 exists in different conformations that favor either trimeric or dimeric IL-2R, resulting in the activation of different immune cells [4].
Upon receptor-ligand binding, the Janus kinase JAK3 phosphorylates JAK1, which in turn recruits SYK (spleen-associated tyrosine kinase). This leads to the phosphorylation and dimerization of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A/B (STAT5A/B). After its translocation to the nucleus, it regulates genes encoding immune-related factors such as IL2RA itself, Treg regulator FOXP3, or suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 or 2 (SOCS1/2). IL-2 also activates the Ras/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways [1,5].
IL-2 therapeutic targeting
In the 1990s, recombinant IL-2 at high dosage became the first US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved immunotherapeutic drug for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and metastatic melanoma [2]. However, its adverse side effects together with its stimulatory action on immunosuppressive Tregs quickly put the brakes on the initial euphoria [3]. Combinatorial therapy of recombinant IL-2 and immune checkpoint targeting monoclonal antibodies (e.g. anti-CTLA4, PD-1) was reported to overcome these off-target effects and improve response rates [2].
Interestingly, low-dose IL-2 therapy has been shown to ameliorate autoimmune diseases and graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) [4]. Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are caused by an imbalance between Tregs and Teffs, both of which are activated by IL-2 [6]. Selective antibodies against IL-2 can alter its conformation, thereby resulting in the selective expansion of Tregs or Teffs subsets [4,6].
Despite its complexity, IL-2-derived therapy remains a promising area of research, with more than 500 clinical trials listed (ClinicalTrials.gov) [7], investigating new and safer IL-2-related reagents in the fight against cancer and autoimmune diseases [2].
References:
1. Pol JG, et al., 2020. Effects of interleukin-2 in immunostimulation and immunosuppression. J Exp Med. 217(1):e20191247.
2. Wrangle JM, et al., 2018. IL-2 and Beyond in Cancer Immunotherapy. J Interferon Cytokine Res.;38(2):45-68.
3. Hernandez R, et al., 2022. Engineering IL-2 for immunotherapy of autoimmunity and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (10):614-628.
4. Trotta E, et al., 2018. A human anti-IL-2 antibody that potentiates regulatory T cells by a structure-based mechanism. Nat Med.:1005-1014.
5. Ross SH, Cantrell DA,. 2018. Signaling and Function of Interleukin-2 in T Lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol.;36:411-433.
6. Yokoyama Y, et al., 2018. IL-2-Anti-IL-2 Monoclonal Antibody Immune Complexes Inhibit Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Augmenting Regulatory T Cell Functions. J Immunol. ;201(7):1899-1906.
7. Raeber et al., 2022. A systematic review of interleukin-2-based immunotherapies in clinical trials for cancer and autoimmune diseases. medRxiv preprint version.