Recombinant anti-mouse IL-1α antibody - Clone 6H7
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 Recombinant mouse mAb against mIL-1α (clone 6H7). For in vitro use. |
Show product |
200 µg |
mil1a-mab9-02
|
|
||
|
Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 InvivoFit™ Recombinant mouse mAb against mIL-1α (clone 6H7). For in vivo use. |
Show product |
1 mg |
mil1a-mab9-1
|
|
Notification: Our anti-mouse IL-1α antibody raised in mice and produced in hybridoma (mabg-mil1a/mabg-mil1a-5) has been removed from our catalog. Its coding sequence has been determined and the antibody is now produced by recombinant technology and purified from CHO cells.
Recombinant mouse IL-1 alpha antibody

Neutralizing monoclonal antibody against murine IL-1α
InvivoGen provides a recombinant fully mouse anti-mouse IL-1α-mIgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that was previously extracted from hybridoma. It is now expressed and produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, ensuring reliability and lot-to-lot reproducibility. Thereby, common hybridoma-related drawbacks such as the generation of non-relevant mAbs containing aberrant light chains are avoided [1].
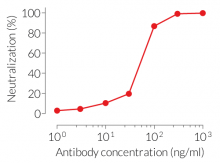
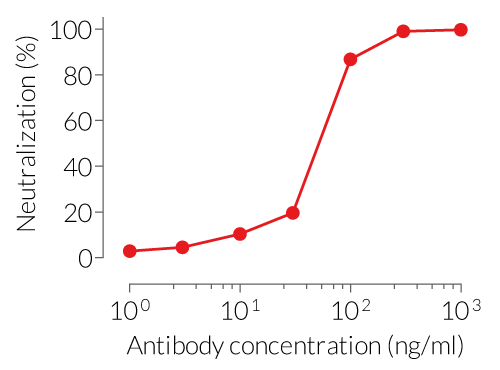
The sequence of Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 is 100% murine (constant and variable regions), as the original clone (clone 6H7) was raised in mice using a proprietary method. This feature allows for reduced immunogenicity and risks of fatal hypersensitivity reactions upon repeated mAb injections into mice [2-4]. Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 neutralizes the precursor and mature form of mIL-1α.
InvivoGen provides this antibody in two grades:
- In vitro use: Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1
- In vivo use: Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 InvivoFit™
All InvivoFit™ products are handled in a clean room, filter-sterilized, and tested for bacterial contaminants. Additionally, this grade guarantees low levels of endotoxins (<1 EU/ml). The buffer formulation is specifically adapted for in vivo studies.
Key features:
- Potent neutralizing activity against the precursor and mature form of mIL-1α (see figure)
- Sequence is 100% murine
- Murine IgG1 isotype (constant region)
- No cross-reactivity with murine IL-1β, human IL-1α, or human IL-1β
- Free from non-relevant mAbs found in hybridoma-based productions
- Produced in animal-free facilities and defined media
- Low aggregation <5%
-
InvivoFit™ grade is available
Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 is designed to efficiently neutralize the biological activity of mIL-1α. Interleukin 1α (IL-1α) is a dual-functional cytokine that can act as a transcription factor or an alarmin triggering local inflammation [5].
References:
1. Bradbury, A. et al. 2018. When monoclonal antibodies are not monospecific: Hybridomas frequently express additional functional variable regions. mAbs, 10(4), 539–546
2. Mall C. et al., 2016. Repeated PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibody administration induces fatal xenogenic hypersensitivity reactions in a murine model of breast cancer. Onco Immunol. 5(2):e1075114.
3. Murphy, J.T. et al., 2014. Anaphylaxis caused by repetitive doses of a GITR agonist monoclonal antibody in mice. Blood. 123(14):2172-2180.
4. Belmar N.A. et al., 2017. Murinization and H chain isotype matching of Anti-GITR antibody DTA-1 reduces immunogenicity-mediated anaphylaxis in C57BL/6 mice. J Immunol. 198:4502-4512.
5. Dinarello CA, et al., 2021. Interleukin 1α: a comprehensive review on the role of IL-1α in the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmunity Reviews, Volume 20, Issue 3.
Specifications
Target: Murine IL-1α (mIL-1α)
Specificity: No cross-reactivity with human IL-1α
Clone: 6H7
Source: CHO cells
Isotype: Murine IgG1, kappa
Control: Murine IgG1 Isotype Control
Formulation of Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1: Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered solution in a sodium phosphate buffer with glycine, saccharose, and stabilizing agents
Formulation of Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 InvivoFit™: Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered solution in a sodium phosphate buffer with 5% saccharose
Tested applications Blocking & Neutralization
Quality control:
- These products have been validated using neutralization cellular assays.
- The complete sequence of these antibodies has been verified.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
- The endotoxin level in Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1 InvivoFit™ is <1 EU/mg (determined by a LAL assay).
Contents
Please note: each mAb is sold separately.
Anti-mIL-1α-mIgG1
- mil1a-mab9-02: 200 µg, lyophilized
Anti-mIL-1Α-mIgG1 InvivoFit™
- mil1a-mab9-1: 1 mg, lyophilized
![]() The product is shipped at room temperature.
The product is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Store lyophilized antibody at -20 °C.
Store lyophilized antibody at -20 °C.
![]() Lyophilized product is stable for at least 1 year.
Lyophilized product is stable for at least 1 year.
![]() Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
InvivoFit™
InvivoFit™ is a high-quality standard specifically adapted for in vivo studies. InvivoFit™ products are filter-sterilized (0.2 µm) and filled under strict aseptic conditions in a clean room. The level of bacterial contaminants (endotoxins and lipoproteins) in each lot is verified using a LAL assay and a TLR2 and TLR4 reporter assay.
Back to the topDetails
Interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α) is a member of the IL-1 family of pro-inflammatory cytokines and plays an important role in the regulation of immune responses. It is constitutively expressed by many cell types, including fibroblasts, keratinocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and T cells. Although, endothelial and epithelial cells are the main source of IL-1α under physiological and pathological conditions [1].
Both IL-1 group members, IL-1α and IL-1β, are expressed as precursors that are further processed into mature secreted forms. However, unlike IL-1β, the pro-form and the mature version of IL-1α show strong biological activities [2]. The pro-IL-1α can be cleaved by several proteases (e.g. granzyme B, caspase-5 and -11, calpain) into a 17-kDa mature form and a 16-kDa N-terminal 'propiece' harboring a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) [1].
Following protease-dependent processing, the mature IL-1α is rapidly secreted through pores of the plasma membrane. There, it interacts with the IL-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1), which is shared with IL-1β. Upon receptor-ligand binding, a structural change of the receptor occurs allowing the co-receptor IL-1R3 to bind and form a trimeric complex [3]. Subsequently, the intracellular adapter protein MyD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response 88) becomes phosphorylated triggering an intricate sequence of (auto-) phosphorylation, complex formation and ubiquitination events. Finally, activated NK-kB, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways induce the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-6 and IL-8 [4].
Indeed, IL-1α is quite unique as it appears to be the only cytokine that could (a) translocate into the nucleus to regulate downstream gene expressions, (b) anchor to the cell membrane to activate IL-1/IL-1R signaling, (c) secrete out of the cell and activate the IL-1/IL1R signaling, and (d) stay in the cytosol with unknown function. The underlying mechanisms that determine and regulate its subcellular dual-functional localization remain a major question in this field [1].
In response to tissue damage or pathogen invasion, IL-1α is either released from dying cells as an alarmin, or exposed on the surface of cells undergoing oxidative or metabolic stress [2]. Due to its role in mediating acute and local inflammation, IL-1α has emerged as a therapeutic target for diseases characterized by tissue or organ inflammation (e.g. myositis, COVID-19, cancer) [1-2].
1. Chiu JW, et al., 2021. IL-1α Processing, Signaling and Its Role in Cancer Progression. Cells. 2021 Jan 7;10(1):92.
2. Dinarello CA, et al., 2021. Interleukin 1α: a comprehensive review on the role of IL-1α in the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmunity Reviews, Volume 20, Issue 3.
3. Dinarello CA, et al., 2018. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev. 281(1): 8–27.
4. Weber A, et al., 2010. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci Signal. 3(105).